Mastoidectomy in Dallas, Fort Worth, Frisco, TX
Mastoidectomy is one of the most common procedures performed in ear surgery. It involves opening the mastoid cavity to achieve a
variety of different surgical goals. In general, mastoidectomy provides access to structures and pathologies of the mastoid, middle ear, ossicles, inner ear, and lateral skull base.
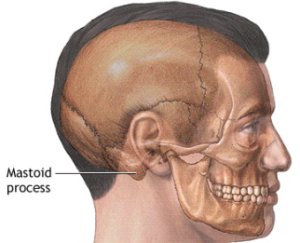
The mastoid is a sinus that lies behind the ear canal and middle ear. It is a pneumatized structure with connections to the air cell system of the entire temporal bone. It is like a beehive in the way it is organized. Often, infections of the ear involve this whole system. In severe cases, mastoiditis occurs, and the infection can spread beyond the mastoid.
The air cells have variable size and number from one patient to another. Those with many large air cells are considered well pneumatized. 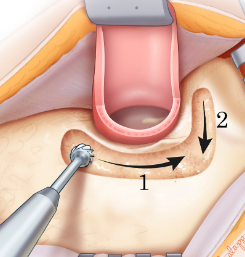 Those with few, small air cells are considered under pneumatized. Under pneumatized mastoids are often found in patients with chronic ear disease.
Those with few, small air cells are considered under pneumatized. Under pneumatized mastoids are often found in patients with chronic ear disease.
Mastoidectomy is performed with a high-speed drill. Larger drill burs are used in the initial steps. As the surgeon progresses deeper into the mastoid, smaller burs are used.
The first step of a mastoidectomy is called a cortical mastoidectomy. This involves simply removing the outer covering of bone. This step along is combined with ear tube placement and antibiotics to treat mastoiditis.
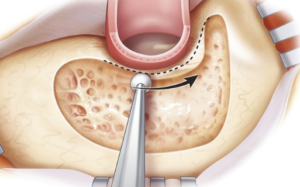
The next step is opening the antrum and locating the ossicles and horizontal canal. The operation is taken to this point to address cholesteatoma or chronic infection associated with eardrum perforation.
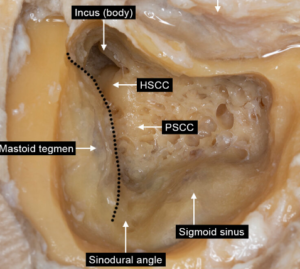
From here a mastoidectomy becomes more tailored to the pathology being treated. If needed, a cochlear implant may be placed through an opening called the facial recess. 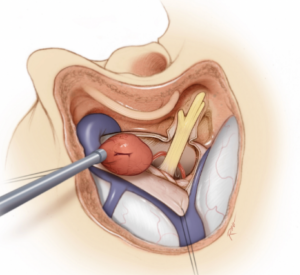 For patients with Meniere’s disease, the endolymphatic sac can be decompressed or a labyrinthectomy can be performed.
For patients with Meniere’s disease, the endolymphatic sac can be decompressed or a labyrinthectomy can be performed.
For patients with superior canal dehiscence, this can be accessed and repaired. Encephaloceles may be reduced and repaired. Mastoidectomy can be combined with skull base craniotomies to allow access for a neurotologist teamed with a neurosurgeon to remove skull base tumors like acoustic neuromas.
Mastoidectomy is commonly performed as outpatient surgery. It is generally safe with minimal risks. Risk and length of stay increase as it is combined with increasingly complex procedures.
In summary, mastoidectomy is a versatile procedure performed by a neurotologist. It can be thought of as a route of access for many different ear pathologies. It is safe, effective, and typically considered outpatient surgery with a few exceptions.

